
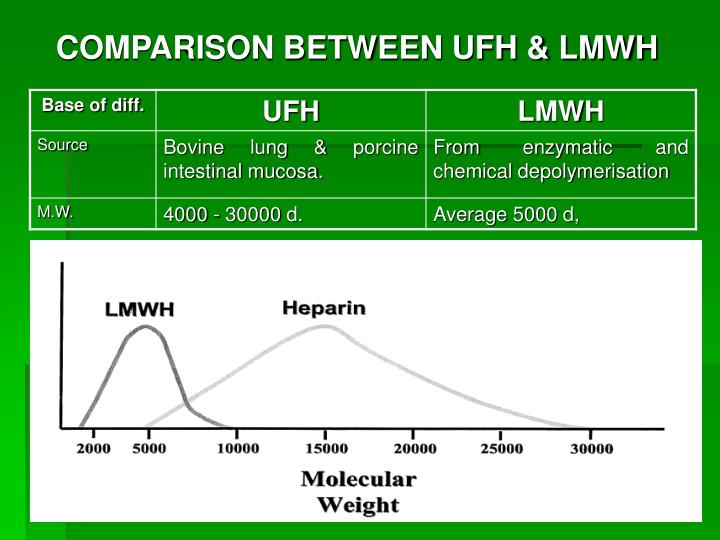
PTT is not an ideal test to monitor heparin. Patients receiving intravenous doses of UFH have historically been monitored with the activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT). This is 150 kg, due to poor absorption, may require monitoring. Fibrin formation can occur when only 5 to 10 nM of thrombin has been produced. The endpoint of a prothrombin time is the conversion of soluble fibrinogen to insoluble fibrin. Altogether, UFH decreases the function of factors XIa, IXa, VIIIa in the intrinsic pathway and factors IIa, Va, Xa in the common pathway.īecause heparin decreases the common pathway, it can mildly prolong the INR. Factor IIa activates the conversion of XI to XIa, VIII to VIIIa, V to Va, and fibrinogen to fibrin. Unfractionated heparin works by binding to antithrombin, causing a conformational change that accelerates antithrombin’s inactivation of IIa (thrombin), Xa and IXa. LMWH is a more homogenous mixture of molecules, with a molecular weight between 40 daltons that preferentially binds to factor Xa in approximately a 3:1 ratio. Heparin complexes with AT, Factor Xa and factor IIa (thrombin) in 1:1 ratio. Unfractionated heparin (UFH) is a heterogeneous mixture of sulfated glycosaminoglycans, of varying molecular weights between 5000 and 30,000 daltons. Both heparin and LMWH are classified as indirect thrombin inhibitors because they inhibit the function of thrombin in the coagulation cascade by binding to antithrombin (AT).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
